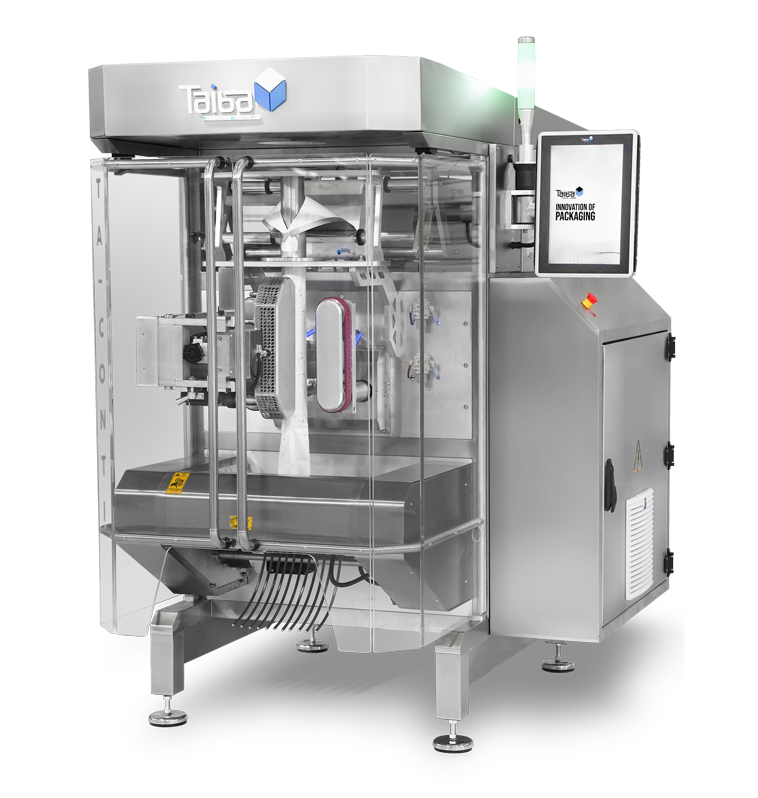
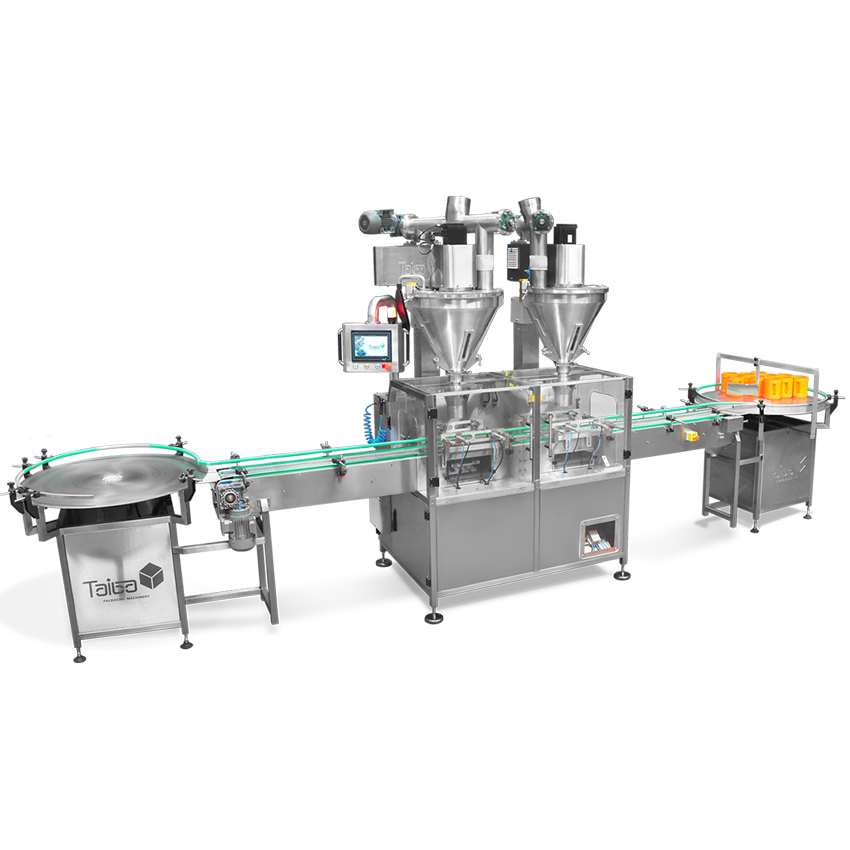
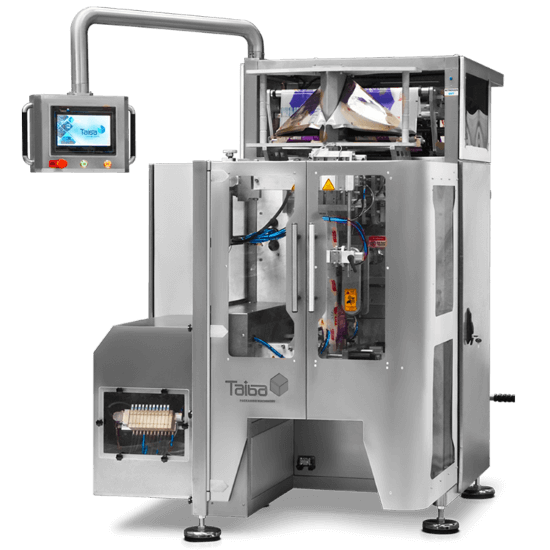
Ürünler
Ne paketlemek istersiniz?Paket Tipleri
Taiba
20
yıllık
tecrübe
TAİBA Packaging Machinery , makinelerinin kalitesi, rekabetçi fiyatları ve satış sonrası müşterilerine sağladığı hizmetler nedeniyle uluslararası şirketlerin saflarına kısa sürede ulaşılmıştır..
Haberler
X